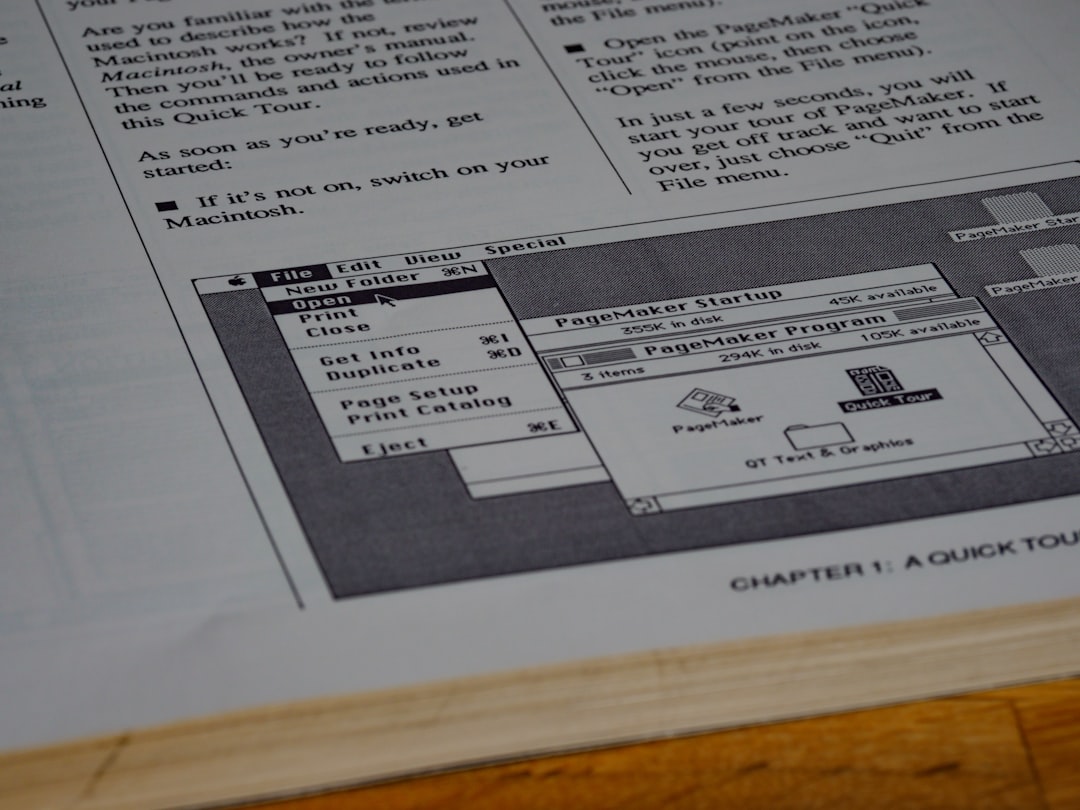
Zero Based Budgeting (ZBB) is a financial management strategy that requires individuals or organizations to justify all expenses for each new period, starting from a “zero base.” Unlike traditional budgeting methods, which often rely on previous budgets as a baseline, ZBB necessitates a thorough examination of every expense, ensuring that each dollar spent is aligned with current goals and priorities. This approach promotes a more disciplined financial mindset, compelling individuals to scrutinize their spending habits and prioritize essential expenditures over discretionary ones. The concept of Zero Based Budgeting originated in the 1970s, primarily within corporate finance, but has since gained traction among personal finance enthusiasts.
The fundamental principle behind ZBB is that every dollar must have a purpose, whether it is allocated to savings, investments, or necessary expenses. This method encourages individuals to think critically about their financial choices, fostering a sense of accountability and control over their financial situation. By adopting ZBB, individuals can gain a clearer understanding of their financial landscape, enabling them to make informed decisions that align with their long-term objectives.
Key Takeaways
- Zero Based Budgeting requires every dollar to be allocated to a specific expense or savings category
- Creating a Zero Based Budget involves listing all sources of income and expenses, and assigning each dollar a purpose
- Tracking expenses and income is essential to ensure that the budget is being followed and to identify areas for adjustment
- Identifying and allocating every dollar means giving each dollar a specific purpose, whether it’s for bills, savings, or debt repayment
- Adjusting and revising the budget is important as circumstances change, and it allows for flexibility and improvement in financial management
Creating a Zero Based Budget
Creating a Zero Based Budget involves several key steps that require careful planning and consideration. The first step is to identify all sources of income, including salaries, bonuses, side hustles, and any other revenue streams. Once the total income is established, the next phase is to categorize all expenses into fixed and variable costs.
Fixed costs are those that remain constant each month, such as rent or mortgage payments, insurance premiums, and loan repayments. Variable costs, on the other hand, fluctuate based on consumption patterns and may include groceries, entertainment, and dining out. After categorizing expenses, the next step in the ZBB process is to allocate funds to each category based on priority and necessity.
This requires individuals to evaluate their spending habits critically and determine which expenses are essential for maintaining their lifestyle and which can be reduced or eliminated altogether. For instance, if an individual finds that they are spending excessively on dining out, they may choose to allocate a smaller portion of their budget to this category while increasing funds for savings or debt repayment. The goal is to ensure that total income minus total expenses equals zero, meaning every dollar has been assigned a specific purpose.
Tracking Expenses and Income
Once a Zero Based Budget has been established, the next crucial step is tracking expenses and income meticulously. This ongoing process allows individuals to monitor their financial activities in real-time and make adjustments as necessary. Various tools can facilitate this tracking, including budgeting apps, spreadsheets, or even traditional pen-and-paper methods.
The key is consistency; individuals should record every transaction promptly to maintain an accurate picture of their financial situation. Tracking expenses not only helps in adhering to the budget but also provides valuable insights into spending patterns. For example, an individual may discover that they consistently overspend in certain categories, such as entertainment or shopping.
By identifying these trends, they can make informed decisions about where to cut back in the future. Additionally, tracking income ensures that any fluctuations—such as bonuses or unexpected expenses—are accounted for in the budget. This proactive approach enables individuals to stay on top of their finances and avoid falling into debt or overspending.
Identifying and Allocating Every Dollar
| Category | Metrics |
|---|---|
| Income | Total monthly income |
| Expenses | Total monthly expenses |
| Savings | Amount allocated to savings |
| Debts | Total outstanding debts |
A cornerstone of Zero Based Budgeting is the principle of identifying and allocating every dollar earned. This means that individuals must assign every dollar of their income to specific categories until there is no money left unallocated. This practice not only fosters discipline but also encourages individuals to be intentional about their financial choices.
For instance, if an individual earns $3,000 in a month, they might allocate $1,200 for rent, $600 for groceries, $300 for transportation, $400 for savings, and so forth until every dollar is accounted for. This meticulous allocation process can also highlight areas where individuals may be overspending or underfunding essential categories. For example, if someone realizes they have allocated too little for healthcare expenses due to an unexpected medical bill in the past month, they can adjust their budget accordingly for future months.
By ensuring that every dollar has a designated purpose, individuals can create a more balanced financial plan that aligns with their goals and values.
Adjusting and Revising the Budget
Flexibility is an essential component of effective Zero Based Budgeting. Life circumstances can change rapidly—unexpected expenses may arise, income may fluctuate, or personal priorities may shift. Therefore, it is crucial for individuals to regularly review and adjust their budgets as needed.
This process involves analyzing spending patterns and determining whether the initial allocations still align with current needs and goals.
Conversely, if they receive a raise or bonus, they might choose to allocate additional funds toward savings or debt repayment.
Regularly revisiting the budget not only ensures that it remains relevant but also reinforces the habit of mindful spending.
Building an Emergency Fund

An integral aspect of financial stability is having an emergency fund in place. Zero Based Budgeting can facilitate the establishment of this safety net by encouraging individuals to prioritize savings within their budget allocations. An emergency fund typically covers three to six months’ worth of living expenses and serves as a financial buffer against unforeseen circumstances such as medical emergencies, job loss, or major repairs.
To build an emergency fund using ZBB principles, individuals should first determine how much they need to save based on their monthly expenses.
For example, if someone’s monthly expenses total $2,000, they might aim to save $500 per month until they reach their target of $6,000.
By treating savings as a non-negotiable expense within the budget framework, individuals can gradually build their emergency fund while still managing other financial obligations.
Paying Off Debt with Zero Based Budgeting
Zero Based Budgeting can be particularly effective for those looking to pay off debt systematically. By allocating funds specifically for debt repayment within the budget, individuals can create a structured plan that prioritizes reducing outstanding balances over time. This approach not only helps in managing existing debt but also fosters a mindset focused on financial responsibility.
To implement debt repayment within a Zero Based Budget framework, individuals should first list all debts along with their interest rates and minimum monthly payments. They can then allocate additional funds toward the highest-interest debts while making minimum payments on others—a strategy known as the avalanche method—or focus on paying off smaller debts first for psychological motivation through the snowball method. By consistently allocating funds toward debt repayment each month until all debts are cleared, individuals can achieve greater financial freedom and reduce stress associated with financial obligations.
Maximizing Savings and Investments
In addition to managing expenses and paying off debt, Zero Based Budgeting provides an excellent framework for maximizing savings and investments. By carefully allocating funds toward savings goals—such as retirement accounts or investment portfolios—individuals can work toward building wealth over time. The key lies in treating savings as an essential expense rather than an afterthought.
Individuals can set specific savings goals within their budget by determining how much they want to save for retirement or other long-term objectives each month. For instance, if someone aims to save $1,000 for a vacation or contribute $500 monthly toward an IRA (Individual Retirement Account), they can incorporate these amounts into their budget allocations accordingly. By prioritizing savings alongside necessary expenses and debt repayment within the Zero Based Budget framework, individuals can cultivate healthy financial habits that lead to long-term wealth accumulation and security.
In conclusion, Zero Based Budgeting offers a comprehensive approach to personal finance management that emphasizes accountability and intentionality in spending habits. By understanding its principles and implementing its strategies effectively—such as creating detailed budgets, tracking expenses diligently, building emergency funds strategically, and prioritizing debt repayment—individuals can achieve greater financial stability and work toward their long-term goals with confidence.
Zero-based budgeting is a powerful tool for managing finances effectively. By assigning every dollar a specific purpose, individuals can take control of their spending and savings. For those looking to streamline their budgeting process, using money management apps can be incredibly helpful. One such app is highlighted in the article “Money Management Apps”, which provides a comprehensive overview of the best apps available for tracking expenses and creating budgets. By incorporating zero-based budgeting principles into these apps, users can optimize their financial planning and achieve their goals more efficiently.